Taxonomy is the science of classifying living organisms into groups based on shared characteristics. It provides a systematic framework that allows scientists, researchers, and students to organize and understand the immense diversity of life on Earth. One of the key aspects of taxonomy is the hierarchy of taxonomic categories. If you are wondering, “Can you identify the correct sequence of taxonomic categories?”, this detailed guide will walk you through the concept clearly and thoroughly.
Understanding the taxonomic hierarchy and the correct sequence is essential for students of biology, competitive exam aspirants, and anyone interested in the natural sciences. In this article, we will delve deep into taxonomy, explain each category, and help you easily identify the correct sequence of taxonomic categories.
What is Taxonomy?
Before answering the main question, let’s understand what taxonomy is.
Taxonomy is the branch of science concerned with classification, especially of organisms. It involves:
- Identification: Recognizing and recording organisms.
- Nomenclature: Giving scientific names.
- Classification: Grouping organisms based on similarities and differences.
The modern system of taxonomy was developed by Carl Linnaeus, who is often called the “Father of Taxonomy.” He introduced the system of binomial nomenclature (two-name system) — for example, Homo sapiens for humans.
Why is Taxonomic Classification Important?
- Organization: It helps scientists organize vast biological diversity.
- Identification: It assists in identifying newly discovered organisms.
- Relationship Understanding: It reveals relationships among different species.
- Ease of Study: It simplifies the study of life forms by arranging them systematically.
Without taxonomy, understanding the living world would be chaotic and difficult.
What are Taxonomic Categories?
Taxonomic categories are different levels in the biological classification hierarchy. They represent ranks or stages used to classify organisms from broad to specific.
Each category is called a taxon (plural: taxa).
The categories are arranged in a hierarchy from the most general to the most specific.
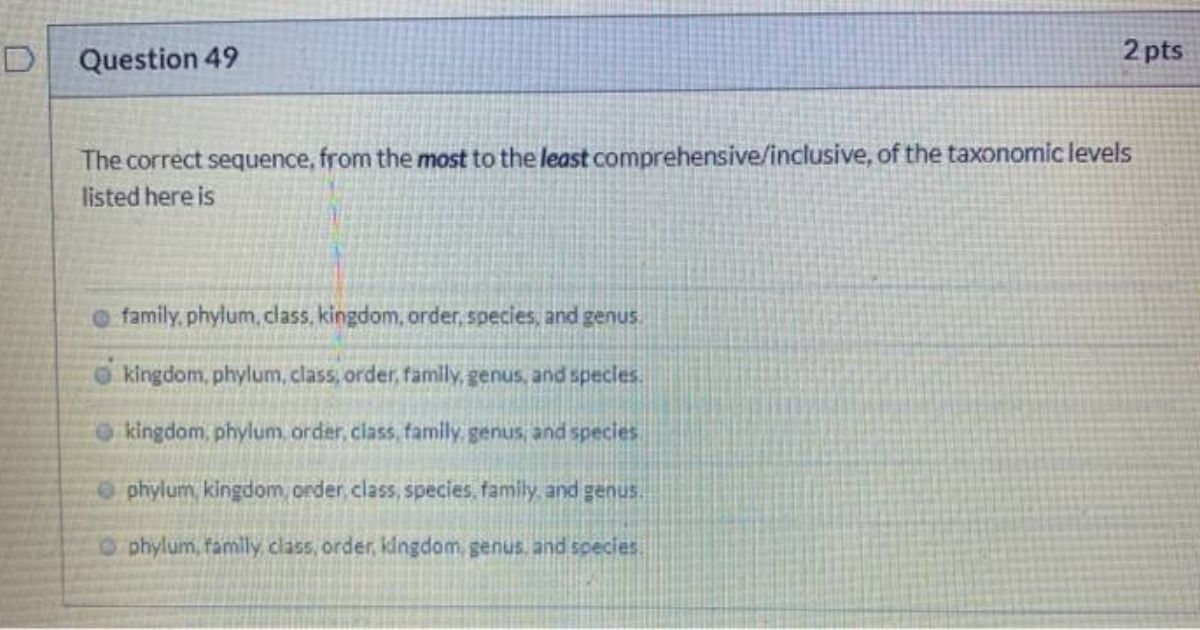
The Correct Sequence of Taxonomic Categories
Now, coming to the most important part: Can you identify the correct sequence of taxonomic categories?
Yes! The correct sequence from highest (broadest) to lowest (most specific) is:
Kingdom → Phylum → Class → Order → Family → Genus → Species
Let’s break it down:
| Rank | Example for Human (Homo sapiens) |
|---|---|
| Kingdom | Animalia |
| Phylum | Chordata |
| Class | Mammalia |
| Order | Primates |
| Family | Hominidae |
| Genus | Homo |
| Species | sapiens |
Easy Mnemonics to Remember the Sequence
Students often use mnemonics to remember the sequence easily. Some popular mnemonics are:
- King Phillip Came Over For Good Soup
- Keep Ponds Clean Or Frogs Get Sick
You can create your own creative mnemonic to memorize it better!
Detailed Explanation of Each Taxonomic Category
Here’s a deep dive into each level:
1. Kingdom
- Highest and broadest category.
- Groups organisms with very basic similarities.
- Examples: Animalia (animals), Plantae (plants), Fungi, Protista, Monera.
2. Phylum
- Groups organisms based on major body plans and structures.
- For plants, the equivalent term is Division.
- Example: Chordata (animals with a backbone).
3. Class
- Organisms within a phylum are further divided into classes.
- Example: Mammalia (mammals that have hair and produce milk).
4. Order
- Classes are divided into orders based on additional similarities.
- Example: Primates (monkeys, apes, and humans).
5. Family
- Orders are broken into families.
- Families group very closely related organisms.
- Example: Hominidae (great apes and humans).
6. Genus
- A genus includes one or more species that are closely related.
- The first part of the scientific name.
- Example: Homo (humans).
7. Species
- Smallest and most specific category.
- A group of individuals that can interbreed and produce fertile offspring.
- Example: sapiens.
Importance of Following the Correct Sequence
Understanding and following the correct taxonomic sequence is crucial for:
- Correct Identification: Helps accurately classify organisms.
- Scientific Communication: Ensures everyone refers to organisms consistently.
- Evolutionary Studies: Shows evolutionary relationships between organisms.
Incorrect sequencing can lead to confusion, misidentification, and mistakes in biological research and studies.
Examples of Correct Taxonomic Sequences
Let’s see some real-world examples:
Example 1: Tiger (Panthera tigris)
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Chordata
- Class: Mammalia
- Order: Carnivora
- Family: Felidae
- Genus: Panthera
- Species: tigris
Example 2: Mango Tree (Mangifera indica)
- Kingdom: Plantae
- Division: Magnoliophyta
- Class: Magnoliopsida
- Order: Sapindales
- Family: Anacardiaceae
- Genus: Mangifera
- Species: indica
Variations in Classification
While the main seven categories remain, scientists sometimes insert subcategories for more precise classification, like:
- Subphylum
- Subclass
- Suborder
- Subfamily
- Subgenus
- Subspecies
These are used when the diversity within a category is very high.
Role of Modern Technology in Taxonomy
In recent years, technology has significantly enhanced taxonomy:
- DNA sequencing helps identify genetic similarities and differences.
- Bioinformatics tools aid in classification.
- Cladistics focuses on evolutionary relationships.
- Molecular taxonomy uses molecular features for classification.
Thus, the traditional sequence remains important but is now supported by advanced scientific techniques.
Common Mistakes in Identifying the Correct Sequence
Many students and even professionals sometimes make mistakes like:
- Mixing the order of categories (e.g., putting Class before Phylum)
- Forgetting intermediate levels like Subclass
- Confusing Genus with Species
Tip: Always start from the largest (Kingdom) and move to the smallest (Species).
Practice Questions
Here are some practice questions to strengthen your understanding:
- Arrange the following in the correct sequence: Family, Species, Order, Genus. Answer: Order → Family → Genus → Species
- In which category does Homo belong? Answer: Genus
- What is the highest taxonomic category? Answer: Kingdom
Conclusion
So, can you identify the correct sequence of taxonomic categories? By now, the answer should be a confident yes!
The correct sequence — Kingdom → Phylum → Class → Order → Family → Genus → Species — forms the backbone of biological classification. Understanding this hierarchy not only helps in academic studies but also gives deeper insights into the marvelous diversity and evolutionary history of life on Earth.
Next time you encounter the scientific name of any organism, you’ll know exactly how it fits into the grand hierarchy of life!